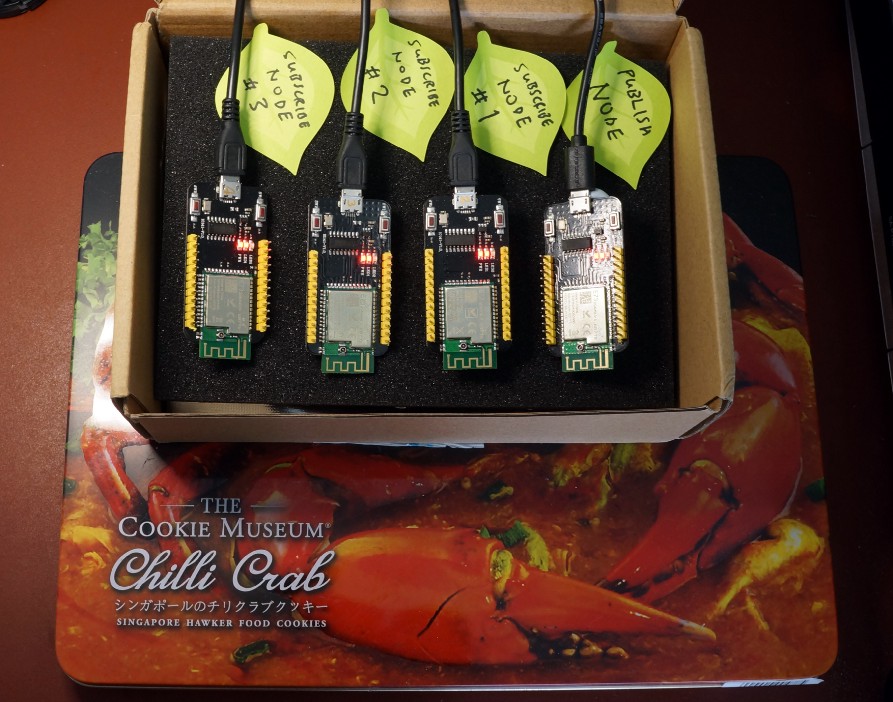
Bluetooth Mesh with four EBYTE E73-TBB Development Boards based on Nordic nRF52832 Microcontroller
Install Bluetooth Mesh and Apache Mynewt for nRF52 and Visual Studio Code on Windows and macOS
Follow these instructions to install the Bluetooth Mesh sample application for nRF52 and Visual Studio Code on Windows and macOS for the article “Bluetooth Mesh with nRF52 and Apache Mynewt”
Install Rust for Windows and macOS
1️⃣ For Windows Only: Click
here to install Build Tools For Visual Studio
2019:https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/#build-tools-for-visual-studio-2019
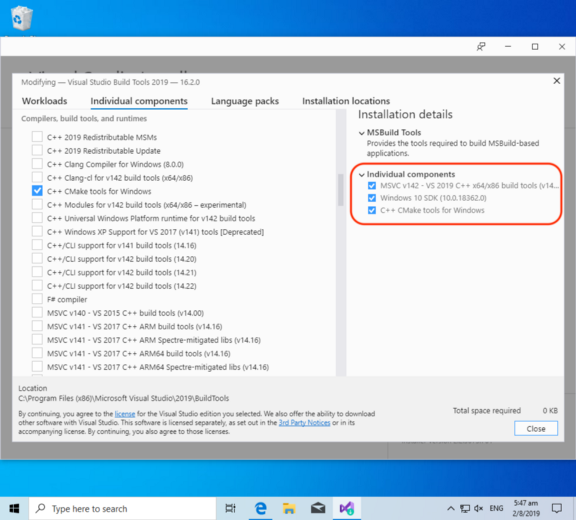
Click the Individual Components tab
Select the following components:
-
Windows 10 SDK (10.0.18362.0) -
C++ CMake Tools for Windows -
(This should be automatically selected)
MSVC v142 — VS 2019 C++ x64/x86 Build Tools
2️⃣ Install rustup according to the
instructions here:https://rustup.rs
3️⃣ For Windows Only: Click
the link provided to download rustup‑init.exe
Launch the downloaded file rustup‑init.exe
If you see the message “Windows Defender SmartScreen prevented an unrecognised app from starting”…
Click More Info
Click Run Anyway
4️⃣ At the Welcome to Rust! prompt, press Enter to
select the default option:1) Proceed with installation (default)
5️⃣ Open the Windows or macOS Command Prompt. Enter into the command prompt:
rustup default nightly
rustup update
rustup target add thumbv7m-none-eabi
rustup target add thumbv7em-none-eabihf
# For RISC-V Only:
rustup target add riscv32imac-unknown-none-elf
rustc -V
The reported version of rustc should be
1.38.0 or later:
rustc 1.38.0-nightly (435236b88 2019–08–01)
Install Source Files
1️⃣ Download the stm32bluepill-mynewt-sensor.7z file attached
below…
For Windows:https://github.com/lupyuen/stm32bluepill-mynewt-sensor/releases/tag/v11.0.0
For macOS:https://github.com/lupyuen/stm32bluepill-mynewt-sensor/releases/tag/v11.0.1
2️⃣ Expand the .7z file with 7zip
(Windows) or Keka (macOS)…
For Windows:https://www.7-zip.org/download.html
For macOS:https://www.keka.io/en/
2️⃣ For Windows Only: Install
Arm Cross-Compiler and Linker for Windows from Arm Developer Website…https://developer.arm.com/-/media/Files/downloads/gnu-rm/8-2019q3/RC1.1/gcc-arm-none-eabi-8-2019-q3-update-win32-sha1.exe?revision=fcadabed-d946-49dc-8f78-0732d2f43773?product=GNU%20Arm%20Embedded%20Toolchain,32-bit,,Windows,8-2019-q3-update
Select this option at the last install step:"Add path to environment variable"
3️⃣ For Windows Only:
Download the ST-Link USB driver from ST-Link Driver Website
(email registration required)…https://www.st.com/en/development-tools/stsw-link009.html
Click Get Software
Unzip the
downloaded file. Double-click the driver installer:dpinst_amd64.exe
4️⃣ Install Windows Studio Code:https://code.visualstudio.com/
Launch Visual Studio Code
Click View → Extensions
Enter cortex-debug
Install the extension “Cortex-Debug” shown below…
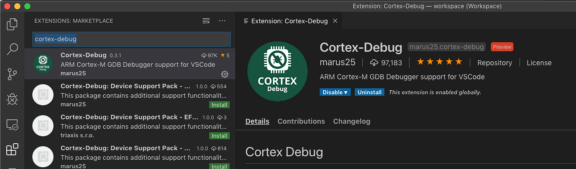
Cortex-Debug Extension
for Visual Studio Code: https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=marus25.cortex-debug
5️⃣ For macOS Only: In Visual
Studio Code, click Terminal → Run Task → Install Mynewt
This installs the Arm Cross-Compiler and Linker for macOS.
Build The Firmware
1️⃣ In Visual Studio Code, click File → Open Folder
Select the
downloaded folder stm32bluepill-mynewt-sensor
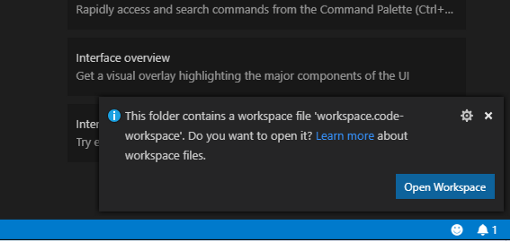
When prompted to open the workspace, click Open Workspace
2️⃣ Click Terminal → Run Task → [1] Build Bootloader
This
builds the Bootloader Firmware, which starts the Apache Mynewt operating system
upon startup. If it shows errors, compare with this build log.
Click Terminal → Run Task → [2] Build Application
This
builds the Application Firmware containing our Rust program. Compare with this build log.
When our Rust program has been successfully compiled as Application Firmware, we should see this…
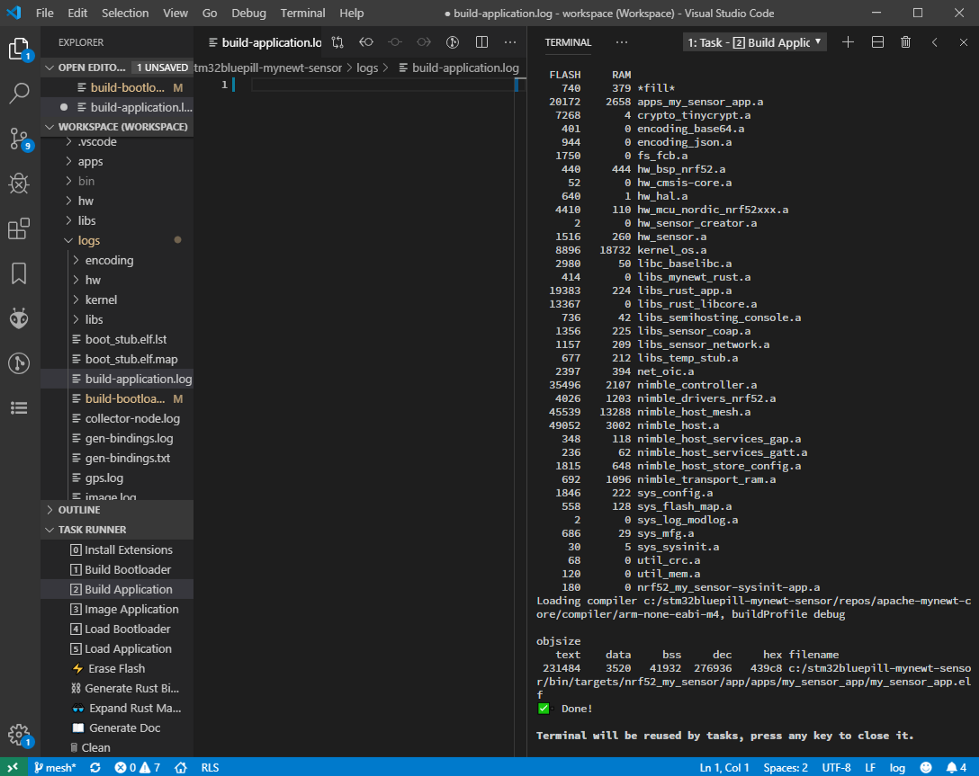
If you see the message Undefined reference to main, rebuild the
application by clicking Terminal → Run Task → [2] Build Application
Click Terminal → Run Task → [3] Image Application
This
creates the flash image from the firmware. Compare with this image log.
If any source files or configuration files are changed, rebuild the application
by clicking Terminal → Run Task → [2] Build Application
Flash The Firmware
The next step is to flash the firmware into ROM. We’ll need to connect the nRF52 to the USB port of our computer via an ST-Link V2 adapter.
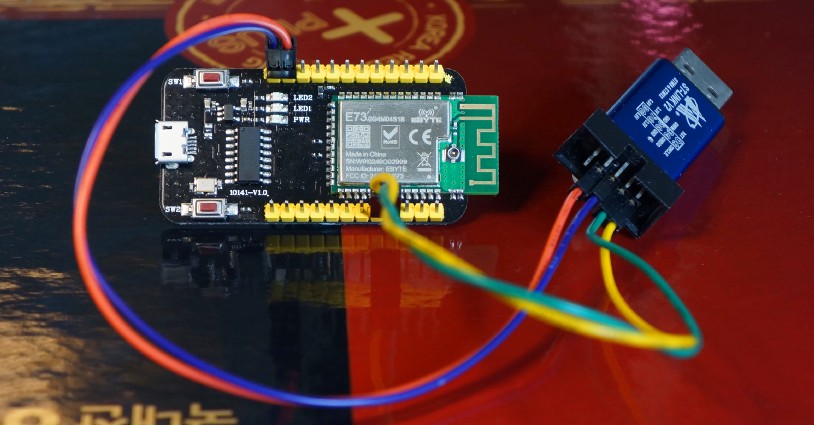
nRF52 Board connected to ST-Link V2
1️⃣ Connect the nRF52 board to ST-Link V2 as follows…
Plug ST-Link into your computer’s USB port.
2️⃣ Click Terminal → Run Task → [4] Load Bootloader
This flashes the bootloader, to start the Apache Mynewt operating system upon startup. If it shows errors, compare with this flash log.
3️⃣ Click Terminal → Run Task → [5] Load Application
This flashes the application firmware. If it shows errors, compare with this flash log.
If you’re unable to flash the nRF52, it’s highly likely that the flash ROM on your nRF52 has been protected. To remove the flash ROM protection, follow the steps in the section “Advanced Topic: Remove nRF52 Flash Protection With Raspberry Pi” in the article “Coding nRF52 with Rust and Apache Mynewt on Visual Studio Code”.
4️⃣ If the nRF52 board has been previously provisioned as a mesh node, erase the
provisioning details in the Flash ROM by clickingTerminal → Run Task → Erase Flash
Then re-flash the Bootloader and Application…
Click Terminal → Run Task → [4] Load BootloaderClick
Terminal → Run Task → [5] Load Application
Run The Program
1️⃣ Click Debug → Start Debugging
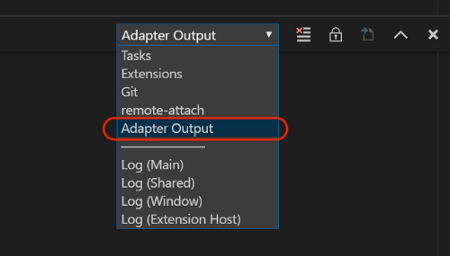
2️⃣ Click View → Output
Select Adapter Output to see the Console
Log of debug messages generated by our program

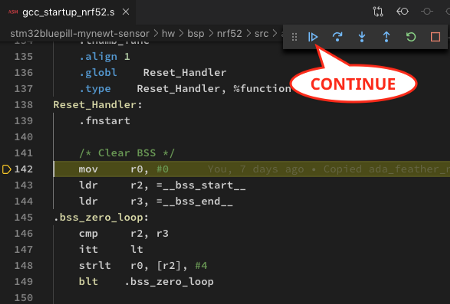
3️⃣ The debugger pauses at Reset_Handler
Click Continue or press F5

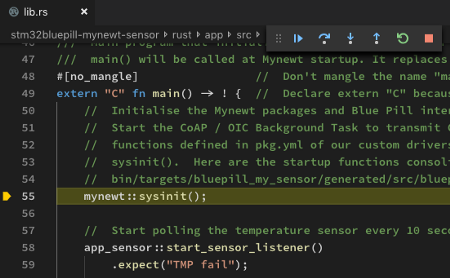
4️⃣ The debugger pauses next at the main()
function
Click Continue or press F5

The program is now running on our microcontroller. The Console Log should look like this.
Console Log from https://github.com/lupyuen/stm32bluepill-mynewt-sensor/blob/mesh/logs/provision-app.log
Here’s a video demo of the application build and debug on nRF52…
Optional: Install Rust Language Server
To get full Rust Language Support for editing Rust source files in Visual Studio Code, you may install Rust Language Server…
1️⃣ In Visual Studio Code, browse to a Rust file like rust/app/src/lib.rs
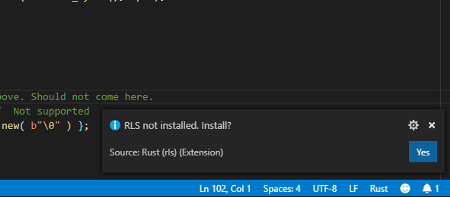
2️⃣ When prompted to install RLS, click Yes

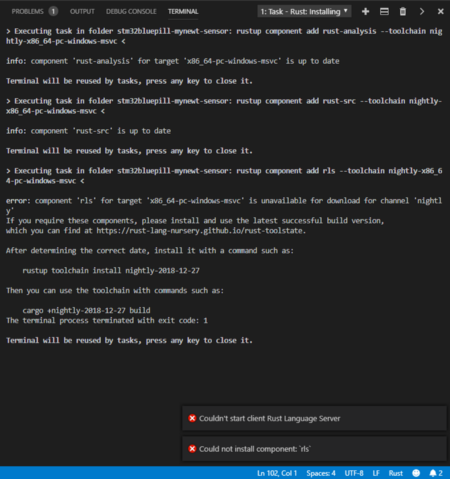
3️⃣ Good Luck! Sometimes the RLS installation fails with this message because we are using the nightly build…